$1.39B Later: Why AI Agents Are Becoming Crypto’s Next Big Layer
$1.39B Later — Why AI Agents Are Becoming Crypto’s Next Big Layer

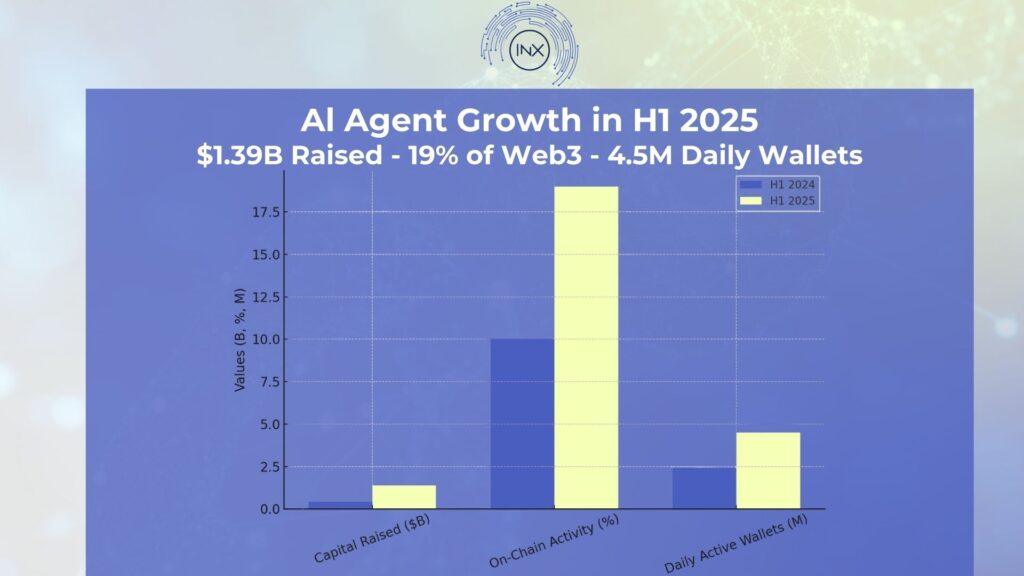
AI agent projects raised over $1.39 billion in the first half of 2025 with their on-chain activity representing about 19% of all on-chain activities. In just six months, AI-related on-chain activity surged by 86%, reaching 4.5 million daily active wallets, and capturing 19% of all Web3 interactions, just behind gaming’s 20%
These numbers signal growing confidence in AI agents, both from institutions and retail investors. In this article, we take a look at what AI agents are, their impact in investing and what the current regulatory landscape looks like.
What Are AI Agents in Crypto?
An AI agent is an LLM-trained model that can make decisions and take action with minimal or no human input. AI agents can continue to train themselves based on available data to become more efficient in their actions.
In crypto, AI agents operate on-chain, interact with smart contracts, and execute tasks on decentralized systems like DAOs, DeFi protocols, or cross-chain bridges. For instance, a trading AI agent deployed on-chain can easily interpret the market. In DeFi, an agent could reallocate liquidity across protocols based on changing yields or risk levels without human intervention.
While AI agents are trained from LLM-based models, they are neither language models nor bots; let’s explain the difference.
AI Agents Vs. Language Models and Bots
Bots are rule-based systems that follow predefined instructions to carry out a particular task. So, you can use it for basic tasks like placing limit orders, sending notifications, or executing trades when a specific price is hit. They’re fast and effective, but they don’t adapt, learn, or make decisions beyond their original script.
Language models like ChatGPT or Claude are built to understand and generate human-like text. Although they can answer questions, interact with humans, and develop strategies, language models can’t carry out actions in real time.
On the other hand, AI agents can make decisions with the ability to operate directly on-chain. Agents can evaluate inputs from the blockchain, make risk-adjusted decisions, and execute transactions without human involvement.
AI Agents in Investing
In many ways, AI agents represent a natural evolution of tools already used in traditional financial markets. Quantitative hedge funds have long relied on machine learning to optimize trade execution, forecast volatility, and identify price anomalies. What AI agents bring is autonomy, the ability to not only analyze market conditions but also to take action without human confirmation.
As expected, adoption is already scaling, big institutions are already using AI agents to manage their assets. BlackRock, for example, uses an AI agent, Aladdin, to assist in managing trillions of dollars in assets. For retail investors, AI agents are a way to improve and become efficient at spotting profitable trades and yield opportunities. Instead of manually monitoring yields across 10 protocols, rebalancing liquidity, or reacting to volatility, investors can task an agent to optimize trading strategy on their behalf.
A 2024 report from Messari highlighted a 30% year-over-year increase in tools supporting agent-based DeFi automation. These include agents that manage LP positions, monitor gas prices, adjust risk thresholds, and respond to market signals autonomously.
AI agents are not only gaining an edge in investing and trading, they have also found application in the blockchain space. In the next section, we talk about how AI agents are used in other areas of Web3.
AI x Broader Crypto Application
Beyond investing and trading, AI agents are also useful in broader blockchain applications like DAO governance and on-chain monitoring. AI agents have been useful for streamlining the often fragmented and manual nature of DAO participation.
AI agents can read proposals, assess tokenomics, and even cast votes based on predefined policy logic. Platforms like Autonolas have already implemented live agents that carry out DAO tasks on behalf of users, offering a more scalable and consistent alternative to manual voting.
Another area AI agents are gaining adoption in is on-chain monitoring; they can act as real-time market observers that can track token flows, market volatility, whale activity, or contract upgrades across multiple chains. Some agents are designed to act like on-chain analysts, issuing alerts or adjusting protocol parameters automatically. While others function like automated compliance officers, tracking for suspicious behavior or activity that falls outside a defined policy scope.
What Investors Should Know about Regulation
Regulations around AI agents remain mostly in the gray area because most regulators haven’t directly addressed autonomous on-chain entities. The European Union is one of the early players in this space; the EU’s AI Act, passed in early 2024, is the world’s first comprehensive AI regulation.

Although the act focuses more on centralized AI services, it could apply to AI agents if they influence financial decisions or interact with consumer assets. Questions around liability, transparency, and auditability remain open, especially in decentralized systems.
In the U.S., the SEC and CFTC haven’t yet issued clear rules around AI agents, but guidance around DeFi, automated investment advice, and consumer protection suggests that scrutiny will increase. Investors should watch for new standards around agent disclosures, permissions, and custodial roles.
Legal uncertainty creates potential risk when it comes to certain situations and introduces a new set of legal and regulatory challenges, like:
- Who is liable if an agent misbehaves?
- How can agents be audited for transparency or fairness?
- What are the legal boundaries for autonomous agents making financial decisions?
For example, if an AI agent makes a harmful decision, like say a DAO treasury exploit, who takes responsibility? the developer, the DAO, or the user?
These kinds of questions are at the core of the next step of the regulatory and legal framework governing AI agents.
AI Agents as the New Layer of Crypto Infrastructure
AI agents are doing more than automating tasks; they have completely changed how investors and protocols interact on-chain. This is just the beginning, as more protocols continue to integrate agent-based systems, we expect that AI agents will become the foundation of interactions on-chain. At that point, active participants within web3 may be defined by their ability to allocate capital, manage exposure, and participate in on-chain activity through agents. At INX, we believe innovation should be accessible without compromising on compliance. We make it easier for both retail and institutional investors to engage with these emerging trends safely and within a regulated environment. Our platform provides access to regulated tokenized assets, giving investors exposure to digital markets through fully licensed pathways.
FAQs & Further Thinking
1. How could AI agents change the competitive landscape between centralized exchanges and decentralized platforms?
AI agents may favor decentralized platforms since they can interact directly with smart contracts without intermediaries. If adoption accelerates, CEXs may need to integrate AI-driven tools to stay competitive, blurring the line between centralized and decentralized ecosystems.
2. What impact might AI agents have on liquidity and volatility in global crypto markets?
By reallocating capital automatically, AI agents could smooth liquidity flows and reduce inefficiencies. On the flip side, if thousands of agents act on similar signals, they could amplify volatility—creating sudden market swings much faster than human-driven trading.
3. Could AI agents eventually collaborate—or compete—with each other in fully autonomous trading environments?
Yes. In theory, AI agents could form networks that negotiate, share liquidity, or hedge risks collectively. Conversely, competition among agents for arbitrage opportunities could result in new forms of “AI-driven market wars,” reshaping price discovery in real time.
4. How might institutional adoption of AI agents reshape the role of human fund managers and analysts?
Fund managers may shift from executing strategies to supervising AI-driven portfolios, focusing on oversight, compliance, and creative strategy design. Analysts could spend more time interpreting macro signals and regulatory shifts while AI agents handle repetitive execution tasks.
5. What ethical dilemmas could emerge if AI agents begin influencing governance decisions across major DAOs?
If AI agents gain significant voting power, they might prioritize efficiency over community values, raising concerns about fairness and decentralization. Ethical debates will likely revolve around whether non-human agents should hold governance rights and how to ensure alignment with human stakeholders.

The INX Digital Company INC September 11, 2025
The INX Digital Company inc. is an expert in the field of finance, crypto and digital securities.






