What is the Bitcoin Lightning Network?
The Bitcoin Lightning Network was created as a scalability solution on the Bitcoin blockchain. It is a layer-2 network built on Bitcoin to facilitate fast and cheap transactions.

Imagine a world where you can send Bitcoin transactions in a second while paying a fraction of the usual fees. That’s the magic of the Lightning Network—a layer-2 solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain to tackle its scalability
Over $78.2 million (around 5000 BTC) was publicly routed on the Lightning Network in August 2023, this represents an enormous growth of over 1212% in two years. In this guide, we cover what exactly is the Lightning Network, how it works, and how you can use it.
What is the Bitcoin Lightning Network?
The Bitcoin Lightning Network (Lightning or LN) is a layer- 2 network on the Bitcoin blockchain built to solve Bitcoin’s scalability issues, namely speed and transaction cost. Lightning Network aims to facilitate faster and cheaper Bitcoin transactions through off-chain transactions.
According to the Lightning Network’s white paper by Joseph Poon and Thadeus Dyja:
“The Lightning network is a decentralized system on which transactions are sent over a network of micropayment channels (a.k.a. payment channels or transaction channels) whose transfer of value occurs off-blockchain.”

Lightning Network was originally introduced in February 2015 by Joseph Poon and Thadeus Dyja and the white paper was published in January 2016. The Beta version of the Lightning Network wasn’t released until 2018 and is being developed by the Lightning Lab
Why the need for the Lightning Network?
While the Bitcoin blockchain is the most decentralized and secure peer-to-peer transaction system, it is not without some limitations. The Bitcoin network is just not that scalable; it can only handle around 7 to 10 TPS, compared to payment systems like Visa that can process up to 65000 TPS or Solana at 2,700 TPS.
The Bitcoin scalability problem can be explained with the Scalability Trilemma, a concept coined by Vitalik Buterin. The Blockchain trilemma refers to the trade-off between 3 key pillars of a blockchain technology – decentralization, security, and scalability.
According to the trilemma, a blockchain can only successfully achieve optimal levels for 2 of the 3 key pillars. Therefore, blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, while decentralized and secure, are not quite scalable. They have to depend on scalability solutions like layer-2 blockchains to manage network congestion.
Lightning Network was built to solve the scalability problem of Bitcoin by reducing network congestion and the cost of transactions. In fact, Lightning Network is expected to reach a throughput of up 1,000,000 TPS meaning that the Lightning Network can process up to 1 million transactions per second.
Since the transactions don’t require block confirmation, transactions on Lightning are near-instantaneous and cost less (lower transaction fees) compared to blockchain transactions. Ultimately, the Lightning network makes Bitcoin practical enough for everyday use and increases its chances of widespread adoption.
How Does the Lightning Network Work?
The Lightning Network operates as a network of bidirectional payment channels that enable instant and high-volume transactions between users.
Rather than recording every transaction on the main blockchain, participants in the Lightning Network create payment channels directly between each other. These channels allow for off-chain transactions, meaning that transactions occur outside of the main blockchain and are only settled on the blockchain when the channel is closed.
The only transactions recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain are the initial creation of the channel and the final settlement between the two parties. All other transactions are recorded off-chain which allows for near-instant transaction speed, more privacy, and lower transaction costs.
The network creates a smart contract between the two parties that acts as the enforcer in the payment channel. It does this by encoding the agreement rules of the payment channel and these rules can’t be broken by either party. All transactions are then moderated by the smart contract and the transaction’s fulfillment is automatic without the need for a third-party.
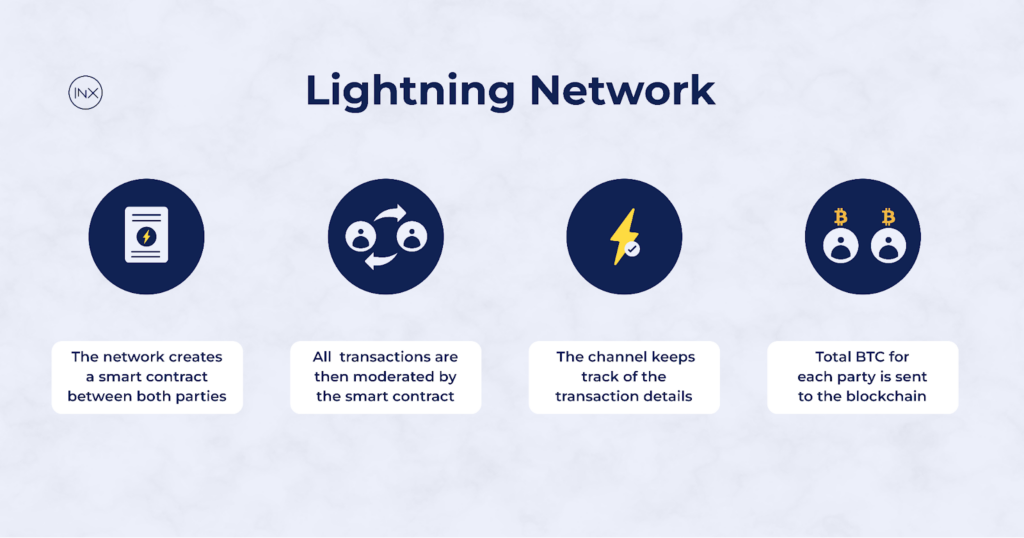
Since the transaction is in a multi-sig wallet, both parties have to sign for transaction confirmation. The payment channels work a bit like a debt settlement card, the transaction within the two parties are not actually exchanging Bitcoin.
Instead both parties sign transactions without their BTC actually leaving their wallets until their channel’s final settlement. The channel keeps track of the transaction details and the total BTC for each person at the end of each transaction. It is the final tally at the end of all the transactions that is sent to the blockchain and recorded.
To explain LN payment channels, let’s use a simple analogy of two business owners – Bob and Alice – who transact often on the blockchain. With traditional Bitcoin transactions, Alice and Bob have to pay transaction fees as often as they transact and might wait up to an hour to confirm their transactions sometimes. A more efficient and cost-saving approach would be for Alice and Bob to open a payment channel on Lightning to process their transactions.
To open their transaction channel, both Alice and Bob deposit some bitcoin in their channel and the Lightning Network creates a smart contract between the both users. Let’s say Alice and Bob deposits 5 BTC each as their security deposit and the following transactions occurs:
- Alice sends Bob 1 BTC; then Alice: 4 BTC, Bob: 6 BTC
- Bob sends Alice 2 BTC; then Alice: 6 BTC; Bob: 4 BTC
- Alice sends Bob 0.5 BTC; then Alice: 5.5 BTC; Bob: 4.5 BTC
- Bob sends Alice 2 BTC; then Alice: 7.5 BTC; Bob: 2.5 BTC
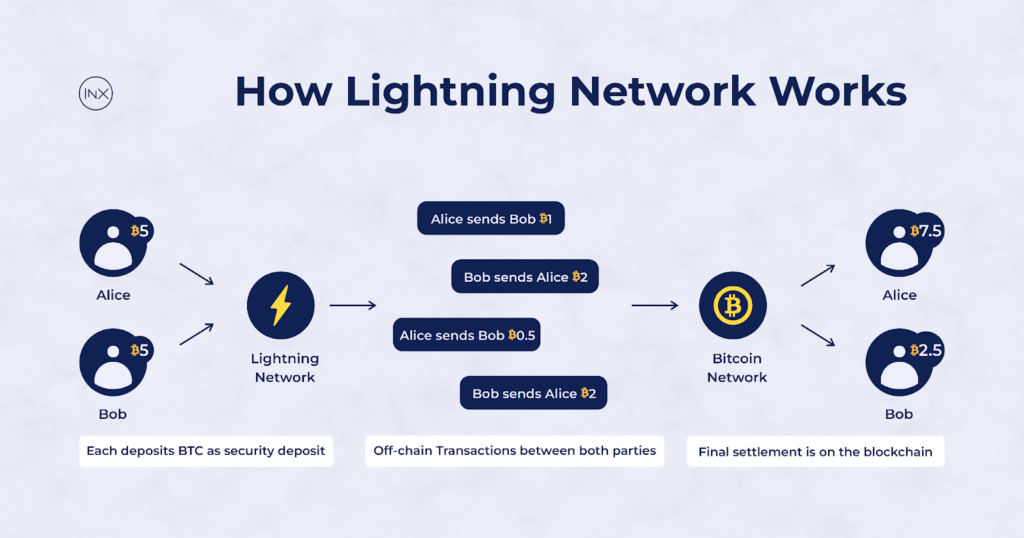
When Alice’s or Bob’s deposit runs out on the channel, they can either close the payment channel or top up their account. If at the end of the week, Bob and Alice decide to close the channel, they send the signed ledger containing the final settlement to the Bitcoin network. This final settlement is recorded on the blockchain as Alice with 7.5 BTC and Bob with 2.5 BTC.
What if Alice needs to send payment to another vendor, John, does she have to open another payment with John?
Not if Bob has a payment channel with John. In order to allow swift payment while avoiding several security deposits to make payment for different vendors, LN allows users to jump payment channels.
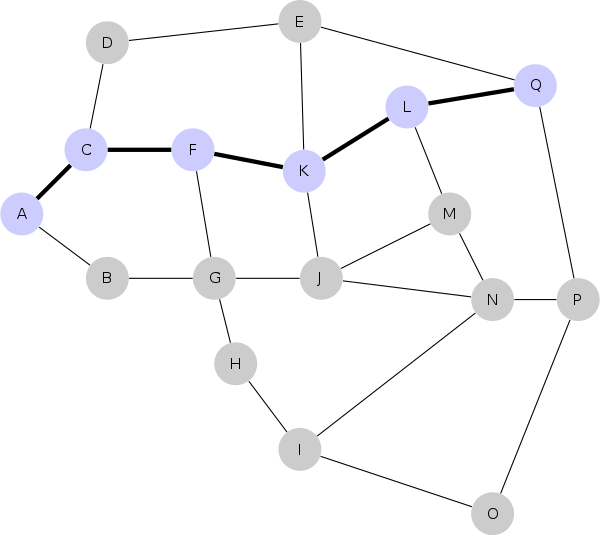
What this means is that Alice can send a payment to John without opening a channel with John by going through Bob. Over time, Alice may be able to transact with anyone on the Lightning Network following the theory of six degree of separation.
In the diagram below A can transact with Q, P, and O despite having direct connection with only B and C
Is the Lightning Network Secure?
The Lightning Network is quite secure with several fraud protection mechanisms in place to prevent one party from taking advantage of the other party in a payment channel. First of all, the payment channel uses a multi-signature wallet that requires both parties to sign each transaction.
Furthermore, each user is expected to drop a security in the form of a BTC deposit in the payment channel which is usually an amount of BTC. But this opens a new form of vulnerability; a party can decide to back out of the channel by simply withdrawing their deposit without informing the other party.
What if Bob decides to withdraw his BTC without telling Alice?
Then he has to wait for 1,000 block confirmation (approximately 1 week) before he gets his 2.5 BTC while Alice gets her 7.5 BTC immediately. In the case, Bob tries to withdraw his full 5 BTC after the 4th transaction without settling Alice, then his full deposit (all his 5 BTC) goes to Alice.
These penalties are in place to prevent fraudulent cases on payment channels. To do this the Lightning Network uses watchtowers to closely monitor transactions. A watchtower is a third party that runs on nodes to monitor and prevent fraudulent closings of a channel.
Other vulnerabilities you might face on the Lightning Network include: Griefing Attack, Flood and Loot, Time Dilation attack, routing attacks and Pining attacks.
Difference Between Bitcoin and Lightning Network
The first thing to note is that the Lightning Network runs on the Bitcoin blockchain and it is supported and secured by the blockchain consensus mechanism. While both the Lightning and Bitcoin network are integral to the Bitcoin ecosystem, they operate differently. Below are
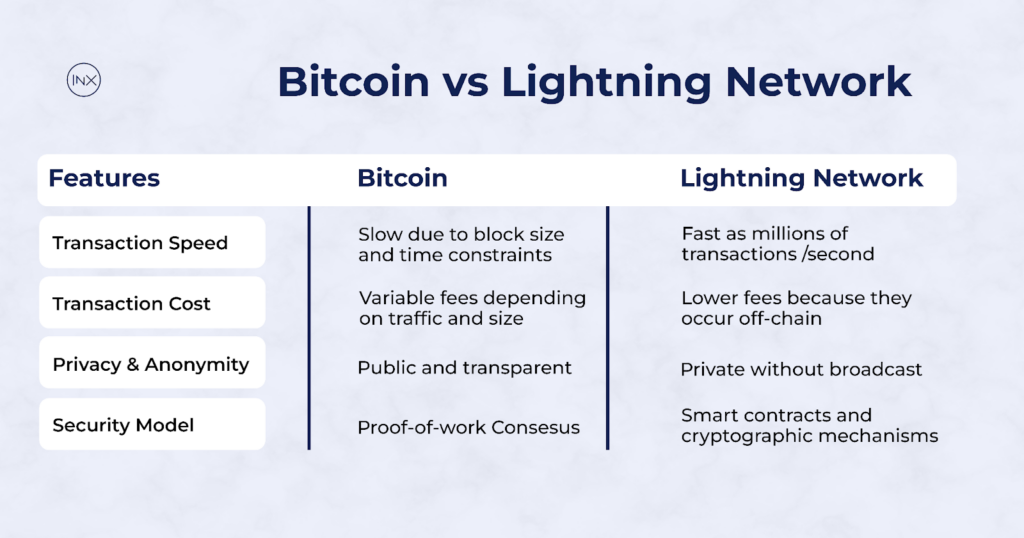
- Transaction Speed and Scalability: Transactions on the Bitcoin Network can take several minutes to hours because of the throughput limitation due to block size and block time constraints. On the other hand, transactions on Lightning Network are near-instantaneous transactions, with the potential for millions of transactions per second, making it highly scalable for microtransactions and high-frequency trading.
- Transaction costs: Bitcoin blockchain transactions may incur variable fees depending on network congestion and transaction size. On the other hand, Lightning Network transactions typically have lower fees since they occur off-chain and do not require miners’ fees for validation.
- Privacy and Anonymity: Bitcoin blockchain transactions are public and transparent, allowing anyone to view transaction details on the blockchain explorer. Lightning Network transactions offer greater privacy since they are conducted off-chain and do not require broadcasting transaction details to the entire network.
- Security Model: Bitcoin blockchain transactions rely on the security of the underlying proof-of-work consensus mechanism to validate transactions and secure the network against attacks. Lightning Network transactions leverage smart contracts and cryptographic mechanisms to ensure security within payment channels, with the underlying security of the Bitcoin blockchain as a safeguard in case of disputes.
Lightning Network in Real Life: Use cases of Lightning
One of the most exciting use cases of the Lightning Network is the facilitation of micro-payment and micro-transactions. The Lightning Network enables instant and low-cost transactions, allowing users to pay tiny amounts for digital content, services, or products. For example, users can stream content, tip creators, or pay for small in-game purchases seamlessly using the Lightning Network.
Since Lightning Network enables fast and cost-effective retail payments, it is suitable for point-of-sale (POS) transactions. Merchants can integrate Lightning Network payment processors into their existing POS systems, allowing customers to pay with Bitcoin instantly and without exorbitant transaction fees. Several businesses have taken advantage of this opportunity to provide fast transactions. According to the Bitcoin Lightning Network directory, at least 233 shops and marketplaces and 147 internet service companies currently support Lightning Network. You can buy over 64,000 goods and services over the Lightning Network. The directory map shows all the businesses that support the Lightning Network.

Crypto exchanges (CEX) can also take advantage of the Lightning Network to offer near-spontaneous withdrawal and fees with lower transaction fees. In fact, several crypto exchanges both CEXs and DEXs already support Lightning for fast withdrawal and deposit transactions.
Lightning Network is also finding traction on social media and blogging platforms. Content creators, including bloggers, podcasters, and social media influencers, can leverage the Lightning Network to monetize their content directly from their audience. By integrating Lightning Network payment solutions into their platforms, creators can receive instant micropayments or tips for their content, bypassing traditional advertising models and intermediary fees. Twitter already integrated the Lightning Network through Stripe to allow users to send and receive tips on the platform.
Lastly, the Lightning Network has gained traction in the gaming industry, particularly within the realm of online gaming and esports. Gamers can use the Lightning Network to purchase in-game items, participate in tournaments, and even wager on esports matches with minimal friction.
How to Use the Bitcoin Lightning Network
While its underlying technology may seem complex, utilizing the Lightning Network is relatively straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use the Lightning Network:
- Set Up a Lightning Network Wallet
The first step in using the Lightning Network is to set up a compatible wallet that supports Lightning transactions. Several wallets, both custodial and non-custodial, offer Lightning Network functionality. Popular options include BlueWallet, Zap, Eclair, and Wallet of Satoshi. Download and install the wallet of your choice from your preferred app store or website.

- Fund Your Lightning Wallet
Once you have installed a Lightning Network wallet, you’ll need to fund it with Bitcoin. This typically involves transferring Bitcoin from your on-chain Bitcoin wallet (e.g., a hardware wallet or a mobile wallet) to your Lightning wallet. Some Lightning wallets also allow you to purchase Bitcoin directly within the app or connect to a Bitcoin exchange to fund your Lightning balance.
- Connect to a Lightning Node
After funding your Lightning wallet, you’ll need to connect to a Lightning Network node to start transacting. Lightning wallets automatically connect to one or more Lightning nodes to route transactions across the network. These nodes act as intermediaries for relaying payments between users. Most Lightning wallets handle node connections automatically, requiring minimal user intervention.
- Initiate Lightning Transactions
With your Lightning wallet set up and connected to the network, you can begin initiating Lightning transactions. Depending on the wallet interface, you may have the option to send or receive payments using Lightning. To send a payment, enter the recipient’s Lightning invoice (a string of characters representing a payment request) and the desired amount. To receive a payment, generate a Lightning invoice within your wallet and share it with the sender.
- Monitor Transaction Status
As Lightning transactions are routed across the network, you can monitor their progress and status within your Lightning wallet. Most wallets provide real-time updates on transaction confirmations, allowing you to track the movement of funds. Lightning transactions typically settle within seconds to minutes, providing near-instantaneous confirmation compared to on-chain Bitcoin transactions, which can take several minutes to hours.
- Close Lightning Channels (Optional)
If you’re using Lightning channels for ongoing transactions, you may eventually want to close them to settle balances on the Bitcoin blockchain. Closing a Lightning channel involves broadcasting a final transaction to the Bitcoin network, which closes the channel and updates the on-chain balances of the participants. Most Lightning wallets offer a straightforward process for closing channels when needed.
Remember that as with any cryptocurrency transaction, it’s essential to practice proper security measures when using the Lightning Network. This includes safeguarding your wallet’s private keys, enabling two-factor authentication if available, and keeping your wallet software up to date. Additionally, be cautious when sharing Lightning invoices and ensure that you trust the sender before initiating payments.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Question)
How do I set up a Lightning Network wallet?
To set up a Lightning Network wallet, download and install a compatible wallet application from your preferred app store or website. Follow the wallet’s instructions to create a new Lightning wallet and fund it with Bitcoin.
Can I use the Lightning Network for large transactions?
While the Lightning Network is primarily designed for smaller, everyday transactions, it can technically support larger transactions as well. However, you may encounter liquidity and routing challenges for larger payments.
Can I use the Lightning Network on mobile devices?
Yes, there are several Lightning Network wallet applications available for mobile devices, making it convenient to send and receive Lightning payments on smartphones and tablets.
Is the Lightning Network compatible with other cryptocurrencies?
While the Lightning Network was initially developed for Bitcoin, there are ongoing efforts to extend its functionality to other cryptocurrencies, such as Litecoin. Cross-chain atomic swaps and interoperability protocols aim to enable Lightning Network transactions across multiple blockchain networks in the future.
How do Lightning Network fees work?
Lightning Network fees are typically minimal and depend on factors such as the size and urgency of the transaction. Fees are paid to node operators for routing payments across the network and are generally lower than on-chain Bitcoin transaction fees.
What happens if a Lightning payment fails?
If a Lightning payment fails to go through, the funds remain in the user’s control and are not lost. Users can attempt to resend the payment or close the payment channel to settle the transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain.
The INX Digital Company INC February 20, 2024
The INX Digital Company inc. is an expert in the field of finance, crypto and digital securities.





