13 Practical Steps to Build a Successful DAO

DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) embody the principles of decentralization, trustlessness, and community governance that Web3 seeks to champion. They play essential roles by enabling decentralized governance and community-driven decision-making.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the significance of DAOs in the Web3 ecosystem, delve into the fundamentals, and provide a step-by-step guide for establishing one.
As a bonus, we have a section that discusses the best practices for effective governance within your DAO with tools/resources to get started.
What is a DAO?
A DAO, or Decentralized Autonomous Organization, is a new organizational structure that operates based on predefined rules encoded as computer programs called smart contracts.
Unlike traditional organizations, which have a centralized governance structure, a DAO is governed by its members in a decentralized manner. It is characterized by the following:
- Decentralized: DAOs operate on blockchain technology, which is inherently decentralized. This means that no single entity or group of entities has complete control over the organization. Instead, power is distributed among its members.
- Autonomous: Once deployed, a DAO operates automatically based on its smart contracts. These contracts execute actions when specific conditions are met without human intervention.
- Organization: At its core, a DAO is an organization, but it operates without a traditional hierarchical structure. Decisions are made collectively by its members, typically through a voting mechanism.
Key Features of a DAO
Governance is executed on a blockchain through predefined rules embedded in smart contracts. It is these smart contracts that define how the organization operates. Below are key features of DAOs that drive how they work.

- Transparency: All decisions, transactions, and changes in a DAO are recorded on the blockchain, making the organization’s operations fully transparent to its members.
- Democratic Governance: DAOs often employ a voting system where members can propose changes or actions, and the community votes to approve or reject these proposals.
- Immutable: Once a decision is made within a DAO, it’s recorded on the blockchain, making it immutable and tamper-proof.
- Token-based Incentives: Many DAOs have native tokens, which can be used to incentivize participation, reward contributions, or represent voting power within the organization.
- Smart Contracts (Trustlessness): DAOs rely on smart contracts for their operations. These contracts automate decision-making, ensuring that rules are executed transparently and in a trustworthy way.
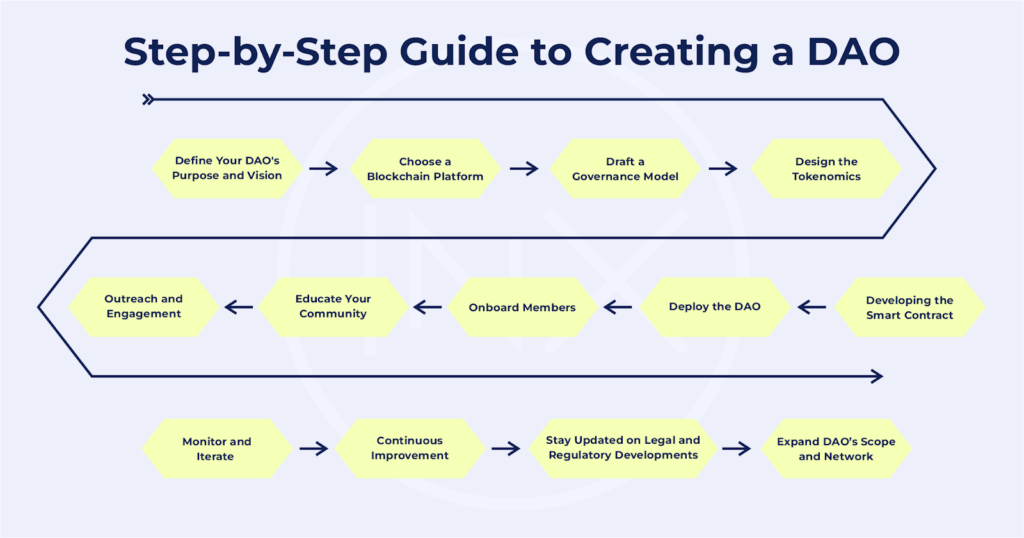
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a DAO
Establishing a DAO involves a series of well-thought-out steps to support a functioning decentralized organization.
This section will break down the DAO creation process into manageable phases, providing Web3 projects with a comprehensive roadmap for creating their own DAO.
Phase 1: Objectives and Scope of DAO
1. Define Your DAO’s Purpose and Vision
Before diving into the technicalities, it’s crucial to understand what you want your DAO to achieve. Start by identifying and defining the goals and purpose of your DAO. Consider questions like:
- What problem does your DAO aim to solve?
- What is the mission statement and vision for your organization?
- What specific projects or initiatives will your DAO undertake?
Your DAO goals could range from decentralized finance (DeFi) projects to community governance and charitable initiatives. This purpose will guide the DAO’s structure, governance model, and smart contract functionalities.
2. Choose a Blockchain Platform
The next step is to select a blockchain that aligns with your DAO’s objectives. Ethereum is the most popular platform for creating DAOs due to its robust smart contract capabilities.
However, blockchains like Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, or Tezos might be suitable, depending on your needs. Research the pros and cons of each platform in terms of scalability, fees, and developer support.
Phase 2: Develop the Governance Model and Tokenomics
3. Draft a Governance Model
At this stage, you’ll determine how decisions will be made within the DAO. Define the rules and procedures for decision-making within your DAO. This includes specifying how proposals are submitted, voted on, and executed. Common models you can adopt include:
- Token-based voting: Members vote using tokens, with more tokens equating to more voting power.
- One-member, one-vote: Each member has equal voting power regardless of their stake or contribution.
- Quadratic voting: Members can vote multiple times on a single proposal, but the cost of subsequent votes increases exponentially.
4. Design the Tokenomics
The next step is determining if your DAO will have its native token. You’ll need to design its economic model. At this stage, decide on things like:
- Total supply
- Distribution methods (e.g., initial coin offerings, airdrops)
- Utility within the DAO (e.g., voting power, access rights)
Remember that tokens represent ownership and voting power within your DAO. Design your tokens carefully, deciding on distribution, utility, and governance rights. Also, the Smart contract should manage token issuance and distribution.
Phase 3: Smart Contract Development
5. Developing the Smart Contract
Smart contracts are the backbone of your DAO, automating its operations and ensuring its rules are followed. Consider the following when developing your smart contract:
- Proposal Creation: Mechanisms for members to submit proposals; how will members submit proposals?
- Voting: How will voting take place? How are votes counted? And how are outcomes determined?
- Funding: If your DAO will distribute funds, how will this be managed?
- Membership: How new members are added or removed.
You can either code your smart contract from scratch or use existing frameworks and templates. However, Smart contracts are the foundation of your DAO, so security is paramount. Conduct thorough audits and testing and ensure thorough testing of your smart contracts to prevent vulnerabilities.
Phase 4: DAO Deployment
6. Deploy the DAO
Once your smart contracts are ready and tested, deploy them on your chosen blockchain platform. This often involves paying a gas fee to deploy your DAO on the blockchain.
7. Onboard Members
With your DAO live, start onboarding members. Depending on your DAO’s design, this could involve a token sale, invitations to stakeholders, or open registration.
Ensure you create a seamless onboarding process for new members. Provide resources, guides, and support to help them understand and participate in your DAO.
Phase 5: Community Building
8. Educate Your Community
Ensure members understand how the DAO operates, how to submit proposals, vote, and other essential functions. This can be done through documentation, webinars, tutorials, or community forums. You can also consider creating explainer articles and videos to introduce your community to blockchain and Web3.
9. Outreach and Engagement
Actively engage with your community. Utilize social media, forums, and developer networks to attract members who share your vision.
Phase 6: Scaling Your DAO
10. Monitor and Iterate
As with any organization, continuous monitoring is crucial. Gather feedback from members, observe how the DAO operates in real-world scenarios, and be prepared to make changes if necessary. This might involve deploying updated smart contracts or adjusting the governance model.
11. Continuous Improvement
Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your DAO’s governance structure and processes. Make necessary adjustments to enhance efficiency and inclusivity.
12. Stay Updated on Legal and Regulatory Developments
The legal landscape for DAOs is still evolving. Stay informed about any regulatory changes in the jurisdictions relevant to your DAO and its members. Consider seeking legal advice to ensure compliance.
13. Expand DAO’s Scope and Network
Consider expanding your DAO’s scope to tackle new projects, partnerships, or initiatives aligned with your mission. Also, leverage network effects by collaborating with other DAOs and Web3 projects. Explore opportunities for cross-pollination and shared resources.
Why Create A DAO for Your Project?
As mentioned earlier, DAOs represent Web3 principles – decentralization, community governance, and trustworthiness. But why should you bother about creating a DAO?
This section discusses some of the reasons why DAOs are essential in Web3.
- Community Involvement: Creating a DAO promotes active community participation and engagement. Members have a direct say in the organization’s direction, which enhances their sense of ownership and commitment.
- Trustless Governance: They facilitate trustless governance by utilizing smart contracts and blockchain technology to ensure transparency and immutability in decision-making.
- Enhanced Security: Security is paramount in the Web3 landscape, and DAOs address this concern with smart contracts. When rigorously audited and implemented correctly, these contracts provide robust security, minimizing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
- Inclusivity: DAOs empower a global community of stakeholders, allowing anyone to participate, propose, and vote on decisions, irrespective of geographic location or background.
- Transparency: All actions and decisions within a DAO are recorded on the blockchain, providing complete transparency and auditability, thus reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
- Immutable Rules: Once established, DAO rules and governance processes are difficult to alter, enhancing security and preventing arbitrary rule changes.
- Global Collaboration: DAOs enable global collaboration on a scale previously unattainable, fostering innovation and cooperation in various industries.
- Autonomy: Once established, DAOs operate autonomously, reducing the need for centralized management and oversight.
- Community-Driven Innovation: DAOs encourage community-driven innovation, enabling projects to evolve in response to their users’ and stakeholders’ needs and desires.
DAOs in Action: Real-World Application of DAOs
While the concept of DAOs might seem new, they have already made significant inroads in various sectors. Here are some real-world applications of DAOs:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DAOs are at the heart of many DeFi projects. Platforms like MakerDAO and Compound are governed by their community members, who propose and vote on changes to the system. This decentralized governance ensures that the platform remains transparent and serves the best interests of its users.
- Content Creation and Curation: Platforms like Steemit and DAOstack allow content creators to be rewarded for their work directly by the community. This peer-to-peer model ensures that creators are fairly compensated and the community genuinely values the content that gets rewarded.
- Open Source Development: Traditional open-source projects often face funding issues. DAOs can provide a solution by allowing community members to fund projects they believe in. Gitcoin, for instance, allows users to fund open-source projects, ensuring that developers are rewarded for their contributions.
Best Practices for Effective DAO Governance
Effective governance is crucial for the success and sustainability of a DAO. Below are best practices to consider when establishing and managing your DAO’s governance structure:
Clear Rules and Procedures
Establish clear rules and procedures for submitting, debating, and voting on proposals. Transparency and predictability enhance trust within the community.

Inclusive Decision-Making
Implement decision-making processes that encourage inclusivity. Consider models like quadratic voting to prevent dominance by a few large stakeholders.
Dispute Resolution
Create mechanisms for resolving disputes and conflicts within the community. An impartial arbitration process can help maintain order.
Security and Risk Management
Prioritize security in your DAO’s operations. Conduct regular security audits and implement safeguards to protect the organization from vulnerabilities.
Education and Onboarding
Provide resources and education to onboard new members effectively. An informed and engaged community is essential for successful governance.
Continuous Iteration
Regularly review and improve your governance processes. Be open to feedback and adjust your rules to address evolving needs.
Tools and Resources For Creating and Managing A DAO
If you’re starting with creating a DAO and unsure how to begin, this section helps with that. Here, we give an extensive list of the tools available to help you create and manage your DAO.

Aragon
Aragon is one of the most popular platforms for creating and managing DAOs. It offers a suite of tools that allow users to create, customize, and govern their DAOs efficiently. Its features include:
- Customizable governance structures
- Token management and distribution
- Voting mechanisms and proposal systems
- Finance management tools
DAOstack
DAOstack is often referred to as an operating system for DAOs. It provides a comprehensive infrastructure for decentralized governance and collaboration. It features the following:
- Alchemy (a native interface for budgeting and resource allocation)
- Arc (a modular Solidity framework for building DAOs)
- Arc.js (a JavaScript library for DAOstack)
MolochDAO
A simple and flexible DAO framework, MolochDAO is designed for grant-making and venture funding. Its offers:
- Minimalistic design for easy setup
- Voting and proposal mechanisms
- Grant distribution and funding tools
Snapshot
Snapshot is a gasless, off-chain, multi-governance client. It’s primarily used for signaling votes within DAOs. It offers:
- Gasless voting
- Supports multiple types of proposals
- Integration with popular wallets
Gnosis Safe
Gnosis Safe is a smart contract-based platform that allows for the creation of multi-signature wallets, making it suitable for DAO treasury management. It features the following:
- Multi-signature wallet creation
- Modular design for flexibility
- Integration with popular Ethereum tools and dApps
Colony
Colony provides a platform for creating decentralized organizations where individuals can collaborate and make decisions based on their contributions. Its features include:
- Task and project management tools
- Reputation system based on contributions
- Financial management and budgeting
Tally
Tally is a governance dashboard for DAOs, providing insights into proposals, voting, and other governance activities. Its features include:
- Governance analytics
- Proposal tracking
- Voting breakdown and insights
Final Thoughts
DAOs are a shift from what we think about the traditional centralized organizational and governance structure. Instead, they offer a glimpse into Web3’s core promise – a future where power is decentralized, decisions are transparent, and communities are at the heart of every organization.
However, as with every innovation at an early stage, there are some limitations, and DAOs are no exception. Security vulnerabilities, participation inequality, and decision-making paralysis are some common issues. However, these challenges can be navigated with a proactive approach. Regular audits, fostering active participation, and setting clear guidelines can mitigate most challenges.Remember that DAOs are not just a passing trend; they’re here to stay. As technology evolves and the world shifts towards a more decentralized model, DAOs will play an increasingly significant role in various sectors. Their potential to revolutionize industries, from finance to governance, is immense.
The INX Digital Company INC October 18, 2023
The INX Digital Company inc. is an expert in the field of finance, crypto and digital securities.





